Configuration¶
Overview¶
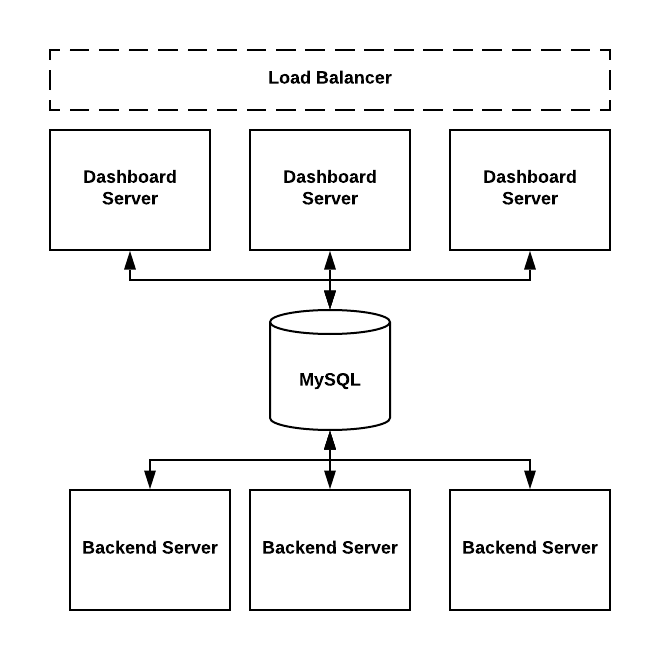
ThirdEye could be deployed on single machine or deployed in clusters.
- Dashboard servers are used to host web applications.
The org.apache.pinot.thirdeye.dashboard.ThirdEyeDashboardApplication class is the entry point.
dashboard.yml and rca.yml are used to configure dashboard servers.
- Backend servers are used to schedule tasks or run the tasks.
The org.apache.pinot.thirdeye.anomaly.ThirdEyeAnomalyApplication class is the entry point.
detector.yml, persistence.yml and data-sources-config.yml are used to configure backend servers.
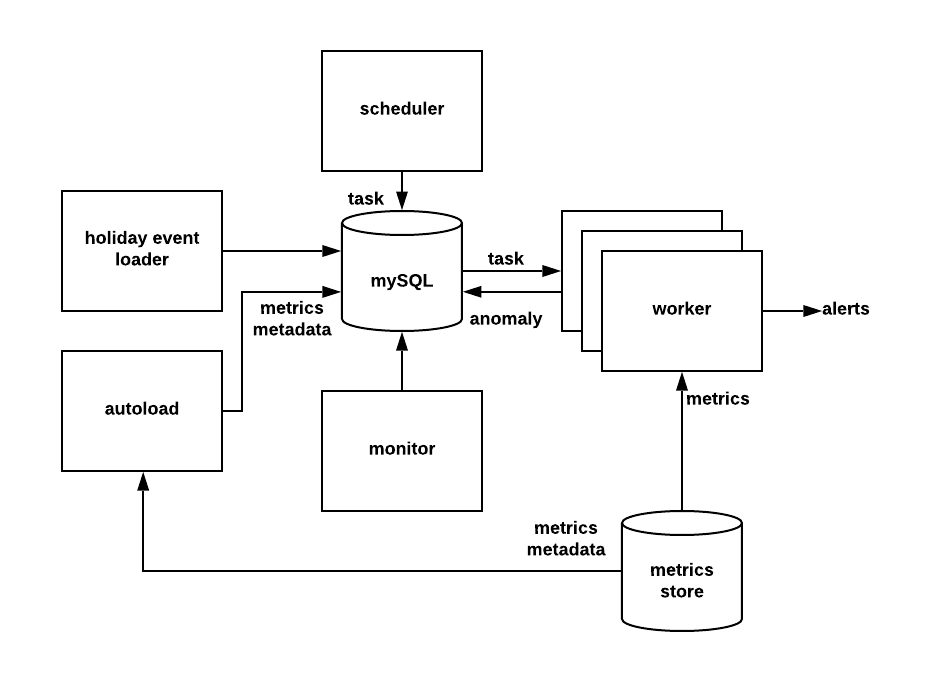
detector.yml¶
ThirdEye uses this file to configure the backend server.
You can deploy ThirdEye to multiple nodes with specific modules enabled in each node.
Here are a list of modules you can configure in this file:
- autoload: Load Pinot metrics metadata automatically.
- holidayEventsLoader: Load holiday events from Google Calendar.
- monitor: Used to do clean up tasks. By default ThirdEye will delete - detection tasks that are older than 30 days and alert tasks that are older than 10 days.
- worker: Handles the actual tasks to do anomaly detection or alerting. You can deploy multiple workers to share the load.
- detectionPipeline: Scheduler to generate detection tasks.
- detectionAlert: Scheduler to generate alert tasks.
To enable one module, you can change the module’s value to “true”.
For example, below configures a node with worker and scheduler enabled.
holidayEventsLoader: false
monitor: false
pinotProxy: false
worker: true
detectionPipeline: true
detectionAlert: true
To have the minimum system running you need to enable “worker”, “monitor”, “detectionPipeline” and “detectionAlert”.
Besides the module configuration you can configure the other followings in this file:
- SMTP configuration: Configure SMTP server which is used to send alert mail.
- Log configuration: SLF4J configurations.
- Server ports: Endpoint ports for backend servers.
- Swagger configuration.
- PhantomJSPath: PhantomJS is used to generate anomaly metrics screenshots which are attached in alert mail.
persistence.yml¶
ThirdEye uses MySQL to store all the metadata. This file is used to configure MySQL database instance.
databaseConfiguration: url: user: password: driver: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver Here is an example:
databaseConfiguration: url: jdbc:mysql:///thirdeye?autoReconnect=true user: te_dev password: xxxxx driver: com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
data-sources-config.yml¶
ThirdEye doesn’t store the actual metrics but will pull the metrics using data source loaders. This file controls the metrics data sources.
Here is an example used in ThirdEye production which connects to two data sources: PinotThirdEyeDataSource and SqlThirdEyeDataSource.
Please note ThirdEye support MySQL data source, and this configuration is different with persistence.yml.
dataSourceConfigs:
- className: org.apache.pinot.thirdeye.datasource.pinot.PinotThirdEyeDataSource
properties:
zookeeperUrl: '<zookeeperurl>'
clusterName: '<clustername>'
controllerConnectionScheme: 'https'
controllerHost: '<hostname>'
controllerPort: <port>
cacheLoaderClassName: org.apache.pinot.thirdeye.datasource.pinot.PinotD2ResponseCacheLoader
metadataSourceConfigs:
- className: org.apache.pinot.thirdeye.auto.onboard.AutoOnboardPinotMetadataSource
- className: org.apache.pinot.thirdeye.datasource.sql.SqlThirdEyeDataSource
properties:
MySQL:
- db:
te: 'jdbc:mysql://<mysqlurl>/thirdeye?autoReconnect=true'
user: 'thirdeye'
password: '<password>'
For more examples on datasource configurations please check Alert Setup.
cache-config.yml¶
Decides which caching scheme(s) to use in ThirdEye for optimizing data fetching process. If applicable, contains settings for a user specified cache data source configuration.
useInMemoryCache: true
useCentralizedCache: false
centralizedCacheSettings:
# TTL (time-to-live) for documents in seconds
ttl: 3600
# if inserting data points individually, max number of threads to spawn to parallel insert at a time
maxParallelInserts: 10
# which store to use
cacheDataStoreName: <cache data source of choice>
cacheDataSources:
<cache data source name>:
className: <class name>
config:
<your config setting>: <value>
<your config setting>: <value>
...
<your config setting>: <value>
<cache data source name>:
className: <class name>
config:
<your config setting>: <value>
<your config setting>: <value>
...
<your config setting>: <value>
# you can add more cache data sources below if you like
The configs for cache data sources are flexible and schemaless, so you can add as many config settings as you need or want. For the most part, these settings will probably be used for connection and authentication configuration settings, like host URI(s) or username/password/certificate files to authenticate to the data source.
dashboard.yml¶
Controls settings relate to web application servers. The followings are configured here:
- LDAP authentication. To enable LDAP authentication, change “authEnabled” to “true”.
authConfig:
authEnabled: true
authKey: <authentication_key>
ldapUrl: <ldap_url>
domainSuffix:
- linkedin.biz
cacheTTL: 3600
cookieTTL: 604800
adminUsers:
- user1
- user2
- Root cause analysis (RCA) configuration: Control thread pool size for RCA pipelines. Default is 5.
- Dashboard host and endpoints configuration.
- Swagger configuration.
rca.yml¶
This configures the RCA pipelines, which is used to either do metrics analysis or loads events from different systems.
These pipelines are called online and not pre-loaded.
Each pipeline derives from org.apache.pinot.thirdeye.rootcause.Pipeline class, and has “inputNames”, “outputName”, “className” and “properties”. One pipeline can take another pipeline’s output as input and it is a DAG.
The “className” is used to create instances using reflection.